Essential Insights
-
New Malware Threat: Cybersecurity researchers have identified "CastleLoader," a versatile malware loader used to distribute multiple types of malware, including information stealers and remote access trojans (RATs).
-
Evasion Techniques: CastleLoader utilizes advanced techniques like dead code injection and packing to impede analysis, enabling it to function as both a delivery mechanism and staging utility for future malware payloads.
-
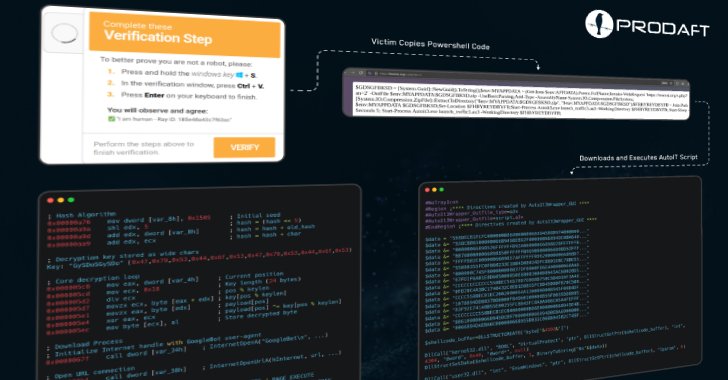
Distribution Strategies: The malware employs social engineering tactics through phishing attacks, fake GitHub repositories, and manipulative web pages to deceive users into executing PowerShell commands that trigger infections.
- Growing Malware Ecosystem: With over 1,634 documented attempts and a 28.7% infection rate since May 2025, CastleLoader represents a significant threat within a cybercrime supply chain, showcasing advanced operational capabilities akin to malware-as-a-service (MaaS).
Problem Explained
In a burgeoning landscape of cyber threats, the emergence of CastleLoader, a sophisticated malware loader, signals a significant evolution in the distribution of malicious software. Identified by Swiss cybersecurity firm PRODAFT, this versatile loader has been instrumental in delivering an array of information stealers and remote access trojans (RATs) through tactics that exploit social engineering, such as Cloudflare-themed ClickFix phishing attacks and counterfeit GitHub repositories mimicking legitimate applications. By employing advanced techniques like dead code injection and dynamic unpacking, CastleLoader complicates the analysis and attribution of its actions, facilitating a more covert and adaptive threat environment. Since its first detection earlier this year, it has inadvertently affected over 469 devices, showcasing a concerning infection rate of 28.7%.
The report, shared with The Hacker News, elucidates the intricacies of CastleLoader’s operational paradigm, underscoring its ability to act as both an initial infection vector and a staging platform for subsequent malware deployment. This dual functionality not only confounds security efforts but also highlights its integration into a broader malware-as-a-service (MaaS) ecosystem, reflecting a strategic shift among cybercriminals towards stealth and modularity. By manipulating trust in software repositories and employing robust evasion tactics, CastleLoader exemplifies the evolving sophistication of cybercriminal infrastructure, making it a formidable adversary in contemporary cybersecurity.
Critical Concerns
The emergence of CastleLoader poses significant risks not only to individuals directly impacted by its malicious activities but also to an array of businesses and organizations that might unwittingly become collateral damage in its wake. This versatile malware loader, adept at executing sophisticated phishing schemes and masquerading as trusted software repositories, creates a ripple effect; as compromised users inadvertently propagate the malware, businesses risk loss of sensitive data, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. The modular nature of CastleLoader enables attackers to easily adapt and evolve their strategies, complicating detection and mitigation efforts for cybersecurity defenses. Consequently, organizations reliant on user trust and data integrity may find themselves vulnerable to breaches that erode consumer confidence and invite regulatory scrutiny, underscoring the need for robust cybersecurity measures across the board to counteract the pervasive threat posed by such advanced malware.
Possible Action Plan
Timely remediation is crucial in counteracting the insidious spread of malware, particularly the CastleLoader strain, which exploits deceptive GitHub repositories and ClickFix phishing schemes to infiltrate a staggering 469 devices. Rapid intervention is essential to mitigate damage and restore security integrity.
Mitigation Steps
- Immediate Isolation: Disconnect infected devices from the network to prevent further spread.
- Threat Detection: Employ advanced threat detection tools to identify remnants of the malware.
- Update Security Protocols: Regularly update antivirus and anti-malware software to the latest versions.
- User Education: Conduct training sessions on identifying phishing attempts and suspicious repositories.
- Patch Management: Ensure all software and systems are regularly patched to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Plan: Activate an incident response team to execute pre-established procedures.
- Post-Incident Review: Analyze the incident to identify root causes and improve future prevention strategies.
NIST Guidance Summary
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) emphasizes the necessity of timely detection and response to security incidents. Specifically, organizations should reference NIST Special Publication 800-61 for detailed incident handling guidelines, which align with best practices for managing malware threats like CastleLoader.
Continue Your Cyber Journey
Explore career growth and education via Careers & Learning, or dive into Compliance essentials.
Understand foundational security frameworks via NIST CSF on Wikipedia.
Disclaimer: The information provided may not always be accurate or up to date. Please do your own research, as the cybersecurity landscape evolves rapidly. Intended for secondary references purposes only.
Cyberattacks-V1