Fast Facts
-
Automatic Password Changes: Google Chrome’s new feature allows its Password Manager to automatically change compromised passwords, enhancing account security and user experience.
-
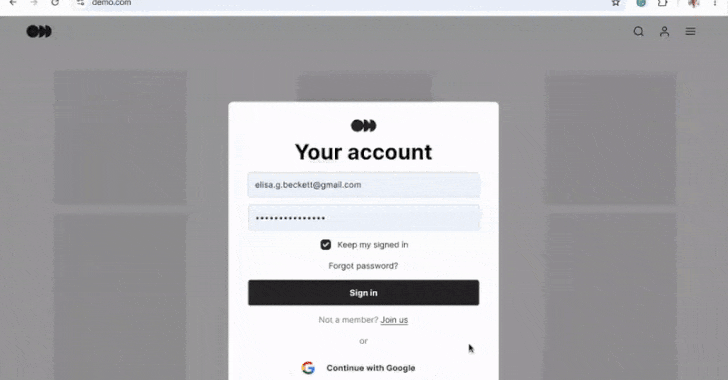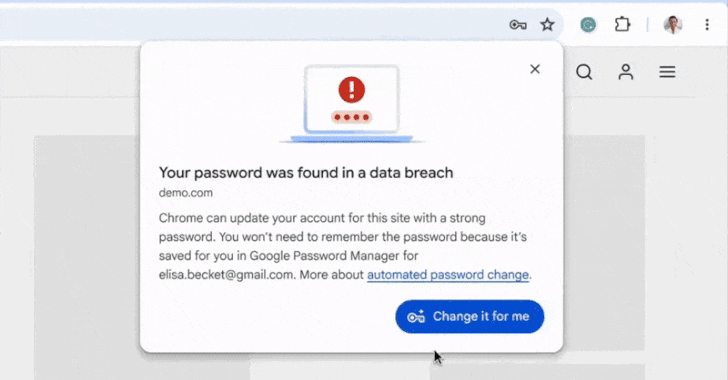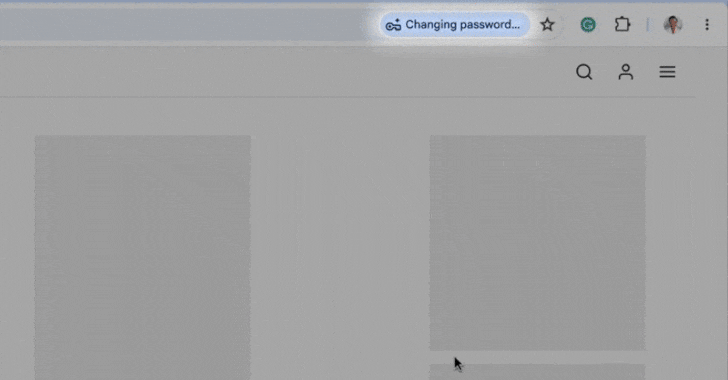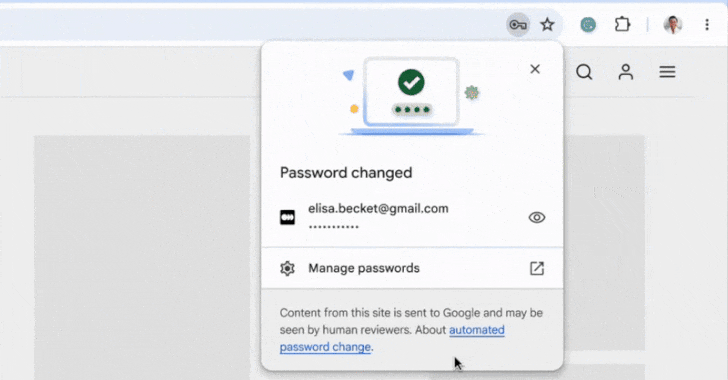
Strong Password Generation: When a compromised password is detected during sign-in, Chrome can create a strong replacement password and update it without user intervention on supported sites.
-
Website Support Requirements: To enable this feature, website owners should implement specific methods such as using autocomplete attributes and setting up a redirect to the password change form.
- Shift to Passkeys: As the tech industry moves towards passkeys for stronger security, this feature is part of broader efforts by companies, including Microsoft, to improve account protection against unauthorized access.
Underlying Problem
On May 21, 2025, Google introduced a significant upgrade to its Chrome browser’s Password Manager, enabling it to automatically change compromised passwords detected during user sign-ins. This advancement, articulated by Google representatives Ashima Arora, Chirag Desai, and Eiji Kitamura, aims to streamline account security by eliminating the cumbersome process users often face when managing compromised credentials. Instead of having to navigate through account settings, users will receive a prompt from Chrome to automatically generate a strong replacement password and update their credentials seamlessly on supported websites.
This enhancement responds to the growing pressures of digital security as tech companies increasingly adopt passkeys as a formidable alternative to traditional passwords. By encouraging website owners to implement specific protocols—such as utilizing autocomplete directives and establishing a standardized URL for password changes—Google aims not only to fortify individual account security but also to facilitate a smoother interrelation between users and online platforms. As this innovation unfolds, it highlights a broader industry trend towards innovative solutions to address vulnerabilities associated with conventional password usage.
Critical Concerns
The introduction of Google Chrome’s automated password change feature presents profound implications for businesses, users, and organizations alike, particularly those vulnerable to data breaches. When a user’s credentials are compromised, and Chrome seamlessly alters their passwords, it may inadvertently create a false sense of security and diminish the urgency for organizations to implement robust cybersecurity measures. If businesses neglect to fortify their own security protocols—such as adopting strong password management practices and ensuring compliance with standards for autofill and password change URLs—they risk heightened exposure to data breaches, resulting in potential financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Furthermore, should users face security breaches on platforms that fail to support Chrome’s feature, the ripple effect could lead to widespread dissatisfaction and distrust, undermining consumer confidence in the affected organizations and prompting users to reconsider engaging with their services altogether. Thus, the interconnectivity of digital security necessitates that all entities remain vigilant and proactive to mitigate collective risks in this ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Possible Next Steps
The recent development of Google Chrome’s ability to automatically change compromised passwords underscores the critical necessity of timely remediation in cybersecurity practices.
Mitigation Steps
- Employ Strong Passwords
- Activate Two-Factor Authentication
- Monitor Exposure Alerts
- Educate Users
- Regularly Update Passwords
- Use Password Managers
NIST Guidance
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) emphasizes the significance of identification, protection, and response to threats. For detailed mitigation strategies, refer to NIST Special Publication 800-63, which provides guidelines on digital identity management to strengthen authentication processes.
Stay Ahead in Cybersecurity
Explore career growth and education via Careers & Learning, or dive into Compliance essentials.
Explore engineering-led approaches to digital security at IEEE Cybersecurity.
Disclaimer: The information provided may not always be accurate or up to date. Please do your own research, as the cybersecurity landscape evolves rapidly. Intended for secondary references purposes only.
Cyberattacks-V1