Quick Takeaways
-
Emergence of Latrodectus Malware: Latrodectus, a new form of malware believed to be a successor to IcedID, utilizes the ClickFix technique to execute in-memory without being detected by security tools, acting as a downloader for ransomware and other payloads.
-
Method of Attack: In recent attacks, users are tricked into executing PowerShell commands from infected sites, where malicious MSI installers sideload a DLL that downloads the main payload without writing files to disk, making detection difficult.
-
Exploitation of Social Media: Recent campaigns leverage platforms like TikTok, where AI-generated videos mislead users into executing malware-laden commands under the guise of activating legitimate software, showcasing how attackers adapt to popular platforms.
- Targeted Cryptocurrency Theft: Malware campaigns have also cloned Ledger Live apps to steal cryptocurrency seed phrases from Mac users, employing malicious scripts to exfiltrate data, demonstrating the evolving tactics of cybercriminals targeting crypto holders.
Underlying Problem
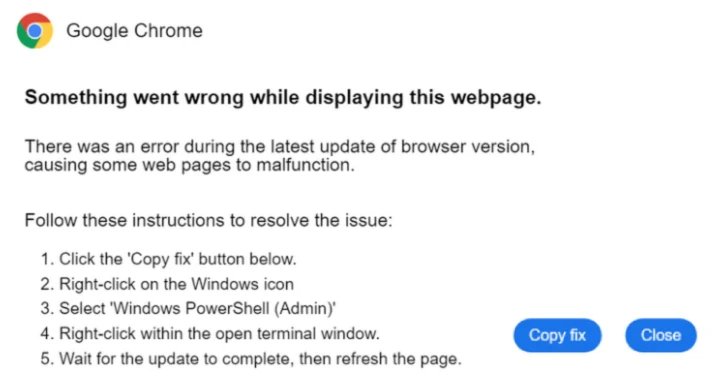
The emergence of the malware known as Latrodectus has captivated cybersecurity circles due to its innovative utilization of the ClickFix social engineering technique, as reported by Expel and disseminated through The Hacker News. Latrodectus, regarded as a successor to IcedID, serves as a downloader for various malicious payloads, including ransomware. Discovered in April 2024 by cybersecurity firms Proofpoint and Team Cymru, it has exploited a critical vulnerability: executing malware directly in memory rather than saving it to disk, significantly decreasing the chances of detection by browsers or security tools. Recent attacks recorded in May 2025 demonstrated how unsuspecting users were manipulated into executing harmful PowerShell commands sourced from compromised websites, thus inadvertently facilitating the malware’s installation.
In a parallel vein, Trend Micro has unveiled a novel campaign that leverages TikTok to disseminate information-stealing malware, such as Vidar and StealC. This approach replaces traditional tactics like fake CAPTCHA pages, using AI-generated videos to coax users into executing harmful commands under the pretext of activating legitimate applications. They guide users through the process of opening Windows’ Run dialog and running malicious scripts, ultimately compromising their systems while amassing significant engagement—evident in one video claiming to enhance Spotify that garnered nearly 500,000 views. These developments underscore a chilling evolution in threat tactics, where attackers are adeptly employing current social media trends to further their malicious objectives, showcasing the ever-shifting landscape of cybersecurity threats.
What’s at Stake?
The emergence of Latrodectus, leveraging the ClickFix social engineering technique, cultivates profound risks for interconnected businesses, users, and organizations. This malware, capable of executing commands directly in memory, bypasses traditional security measures, rendering defenses ineffective. As unaware users inadvertently download malicious payloads, organizations could face significant data breaches, reputational damage, and consequential financial losses. The cascading effect of such breaches not only affects the directly targeted entities but could also jeopardize supply chains and customer trust across entire industries, creating a fertile ground for further exploitation as adversaries adapt to shifts in security postures. Therefore, proactive measures, such as disabling certain system functions and educating users about emerging threats, are imperative to mitigate the pervasive ramifications of this sophisticated malware.
Possible Next Steps
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the imperative for timely remediation cannot be overstated, especially in light of novel malware distribution methods like the ClickFix technique utilized by hackers exploiting TikTok videos to propagate Vidar and StealC malware.
Mitigation Steps
- User Education: Train users to recognize phishing attempts and malicious content on social platforms.
- Endpoint Protection: Implement advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to identify and neutralize threats.
- Content Filtering: Employ web content filtering technologies to restrict access to known malicious sites and links.
- Monitoring Tools: Utilize logging and monitoring to detect unusual behavior indicative of malware activity.
- Patch Management: Ensure all systems and applications are regularly updated to mitigate vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and simulate incident response protocols to ensure swift action against identified breaches.
NIST CSF Guidance
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) emphasizes the necessity of a robust framework to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks. Specifically, refer to NIST SP 800-53, which outlines comprehensive security and privacy controls that organizations should implement to effectively address threats posed by malware distribution tactics.
Advance Your Cyber Knowledge
Stay informed on the latest Threat Intelligence and Cyberattacks.
Explore engineering-led approaches to digital security at IEEE Cybersecurity.
Disclaimer: The information provided may not always be accurate or up to date. Please do your own research, as the cybersecurity landscape evolves rapidly. Intended for secondary references purposes only.
Cyberattacks-V1